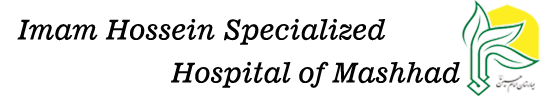Inguinal Hernia
Definition
A hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine, protrudes through a weak spot in the body cavities like abdominal muscles, thorax, skull and spinal cord. Here, we consider a hernia in abdominal muscles called inguinal hernia.
Abdominal hernia has different types:
- Inguinal Hernia: You’ll likely see a lump in your groin or scrotum. It is much more common in men than women.
- Femoral Hernia: You might see a lump into the upper thigh. It is much more common in women than men.
- Incisional Hernia: After surgery in which a doctor must make an opening through your belly, you might get an incisional hernia.
- Umbilical Hernia: it shows up as a lump near the belly button. Less common types in abdominal muscles include epigastric hernia, Spigelian hernia, diaphragmatic hernia and others such as obturator, cystocele and rectocele hernias.
The resulting bulge can be painful, especially when you cough, bend over or lift a heavy object. The disease isn't necessarily dangerous. It doesn't improve on its own, however, can lead to life-threatening complications. It is likely to recommend surgery to fix a hernia that's painful or enlarging. Hernia repair is a common surgical procedure. All hernias usually need surgery to fix them exception umbilical hernia for those less than 4 years old and groin hernia for those who are old or can't tolerate the surgery.
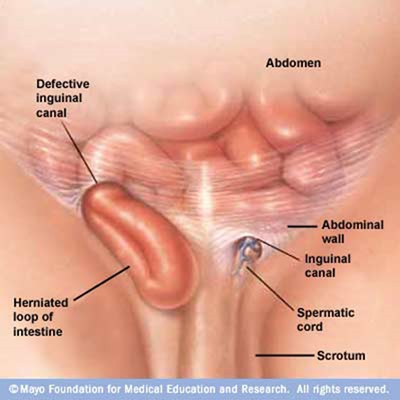
Symptoms
Some hernias have no symptoms and only can be detected by medical examination. The bulge can be observed when you stand, cough or strain.
- A bulge in the area on either side of your pubic bone, which becomes more obvious when you're upright, especially if you cough or strain.
- Pain or discomfort in your groin, especially when bending over, coughing or lifting.
- A burning or dragging sensation in the bulge.
- Pain and swelling around the testicles and the scrotum in men.
- A painful bulge in your groin or scrotum.
- A painful bulge in children.
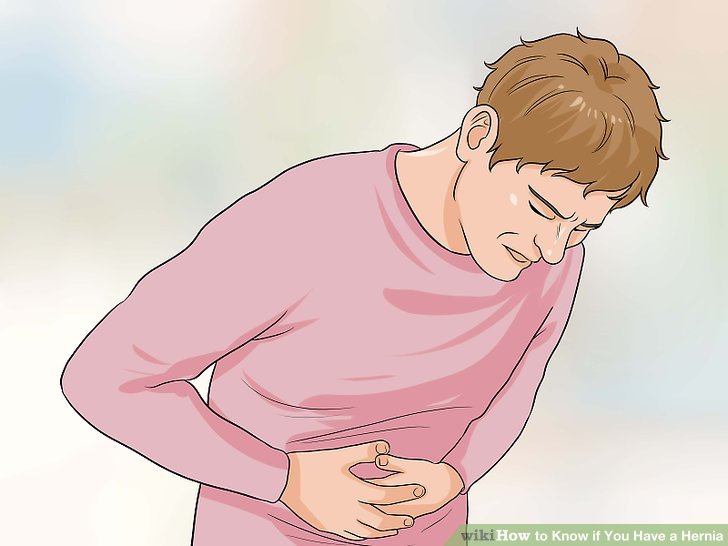
Causes and risk factors
Hernias usually have no apparent cause. But they might occur as a result of:
- Increased pressure within the abdomen due to heavy exercise or lifting
- A pre-existing weak spot in the abdominal wall
- Straining during bowel movements or urination
- Strenuous activity
- Pregnancy
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Obesity
- Being male
- Family history
- Presence of fluids in abdomen
- Smoking
- Chronic constipation and pressure during urination
- Enlarged Prostate
- Previous surgical incision in abdomen
- Cystic fibrosis
- Undescended testicles. Sometimes, hernia is seen with undescended testicles especially in children.
Complications
- Pressure on surrounding tissues. In men, large hernias can extend into the scrotum, causing pain and swelling.
- Incarcerated hernia. If the contents of the hernia become trapped in the weak point in the abdominal wall, it can obstruct the bowel, leading to severe pain, nausea, vomiting, and the inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas. An incarcerated hernia can cut off blood flow to part of your intestine. Strangulation can lead to the death of the affected bowel tissue. A strangulated hernia is life-threatening and requires immediate surgery.
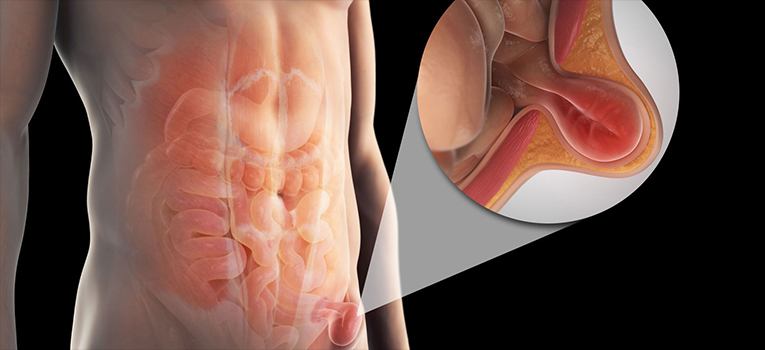
Diagnosis
A physical exam is usually all that's needed to diagnose an inguinal hernia. Your doctor will check for a bulge in the groin area. Because standing and coughing can make a hernia more prominent, you'll likely be asked to stand and cough or strain.
Surgical treatment
In open hernia repair, the surgeon makes an incision in your hernia site and pushes the protruding tissue back into your abdomen. The surgeon then sews the weakened area, often reinforcing it with a synthetic mesh (hernioplasty). The opening is then closed with stitches, staples or surgical glue. After the surgery, it might take 4 to 6 weeks before you're able to resume normal activities.
In laparoscopy procedure, the surgeon operates through several small incisions in your abdomen. People who have laparoscopic repair might have a quicker return to normal activities. This procedure is not a best choice for people having big hernia or previous abdominal or pelvic surgeries.
Supportive treatment
- Rest
- Anti-inflammatory drug intake
- Special stretching & endurance exercises
- Use of hernia truss when surgery is not allowed
- Use of ice chips
Prevention
- Avoid weight gain
- Emphasize high-fiber foods.
- Avoid heavy lifting
- Stop smoking.
Preoperative care
- Stop smoking at least for 4 weeks to reduce probability of chronic bronchitis
- Weight loss to reduce surgical cutting
- Taking a bath a day before surgery
- Hair removal in nearest time before surgery
Postoperative care
- The patient will be encouraged to move about as soon as possible.
- The patient should be examined for urinary retention, infection, hematoma and swelling
- The patient should lift objects gently up to 2 weeks
- The patient should resume normal activities and exercise gradually after 2 weeks to obtain fitness.
Patient guide after discharge
- In case of sneeze or cough, hold the incision site tightly by your hands to avoid severe pain as well as protect the incision site against abdominal pressure
- In case of fever, pain, secretion or high burning, see the doctor.
- The patient should not lift heavy objects 4 to 6 weeks after surgery.
- To reduce swelling and pain, ice chips can be used.
- The patient should eat fresh vegetables &fruits and drink plenty of fluids to avoid constipation. The patient should drink a glass of water on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Drink 2 litters of liquids daily
- All stitches will be removed 7 to 10 days after surgery. To remove them, the doctor should be consulted
- Try to keep the incision site clean.
- In 24 to 48 hours after surgery, the patient may has pain and swelling in scrotum. In this case, put a rolled towel under testicle and then put ice chips on that area for 5 minutes. In case of severe pain, see the doctor.
References
- Inguinal Hernia. Mayoclinic.2013
- Inguinal Hernia. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health.2008
- Inguinal Hernia. Iran Clinic Online
ISO 9001 Certification for Quality Management System &
Certification of Iran National Hospital Accreditation with Excellent Grade
Teaching Patients about
Inguinal Hernia
Prepared by: Quality Improvement, Education and Research Office
Voice Costumer Service (For Complaints, compliments and comments)
SMS: 30001845
Pursuance: Hospital Management
Add: Iran, Mashhad, Shahid Mofatteh Street, Vahid Street, Vahid 3 Alley.
Phone: 32877001